
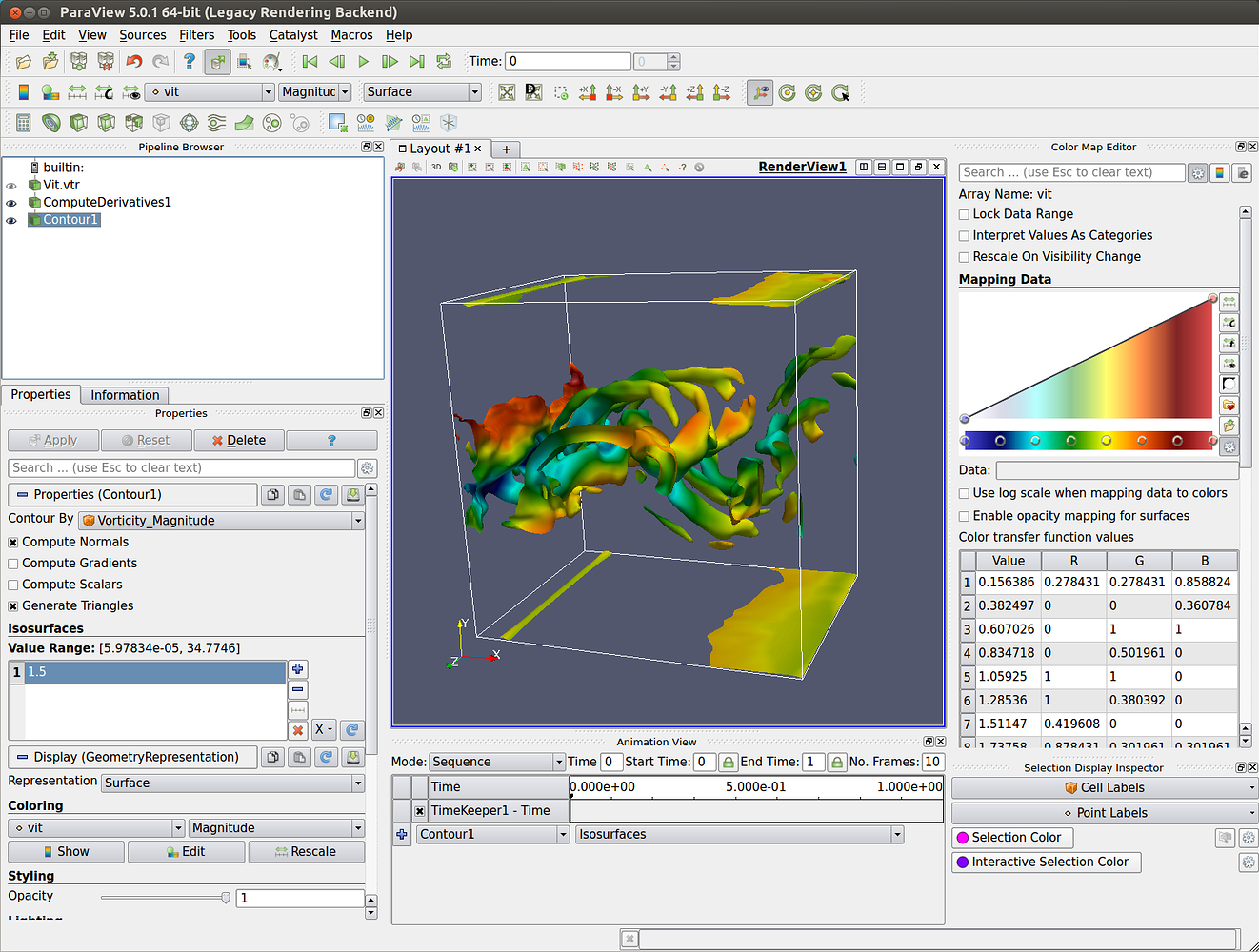
In the "Glyph Properties" window, make the following settings:.Choose icon to add "Glyph" in the tool bar (it is also in the "Filters" menu along with many more options).Open the exported particle VTK files in ParaView (as described above).The most advanced particle plots use glyphs. (for tensor or vector quantities, choose the component to plot from the second menu). Choose simulation result to plot from menu in second row of tool bars.Once you have a plot, you can click and drag with mouse to change the viewing position.The plot should appear when you click "Apply: to finish the opening. Furthermore, the cells are transformed to reflect the particle deformation. The preferred visualization to exported to an unstructured grid ( -U option in ExtractMPM) where each material point becomes a cell in the grid. This section gives to examples to get started with particle plots. Once have one of these plots visible, you can explore all the ParaView options for more ways to visualize the results.īy extracting particle data to VTK files (either using the "Export Particle VTKs." option in NairnFEAMPM or in NairnFEAMPMViz or by running ExtractMPM on a command line), you can also use ParaView to view particle-based plots. The following sections gives to steps to get started with plotting. The available options will depend of if you opened particle VTK files or grid-based VTK files. Once opened, you have many plotting options available. To read them, click the "Apply" button in the object inspector. ParaView does not actually read files when they are opened.You need to open as a block to get movies of results. Alternatively, you can expand the block and select a single file. ParaView will let you select such files as a block and will open them all at once.
PARAVIEW CLUSTER ARCHIVE
If you used VTKArchive Custom Task to archive results for a single material type, the fille name will change to "MPM_mat_#_#.vtk" where the first number is a material number. Those created by a VTKArchive Custom Task will also be in the archived results folder with the naming style "MPM_#.vtk" where "MPM" is the root name you used for the calculation's archived files and "#" is the step number. Those exported as particle VTKs will be in the the archived results folder for your simulation and will have the root name you choose when exporting the files. To open either type of VTK files in ParaView, choose the open command and select a block of VTK legacy files.These VTK files can be used to create grid plots. Save the quantities you might want to plot and one of them should be mass (because it is used in many plot options). Include the VTKArchive Custom Task to save results as VTK legacy files.These VTK files can be used create particle plots. it works best if you include "meansize" which means the simulation included "size" in the archived results. After a simulation is done, use the "Export Particle VTKs." option to extract results of any simulation to particle VTK files.You have two options for visualizing results in ParaView: It is available for many platforms and can run in parallel (hence the name) if installed on a multiprocessor system or cluster of computers. This section gives the basic steps needed to start using ParaView to visualize material point method output from NairnMPM.
PARAVIEW CLUSTER CRACK
2.4 Combining Particle Plots with Crack Plots.2.3 Particle Plots using Point Gaussians.
For help on submitting jobs to the queue, see our SLURM User’s Guide. Your SLURM executables, tools, and options may vary from the example below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
